Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Special Provisions for States in India
Syllabus- Polity and governance [GS Paper-2]
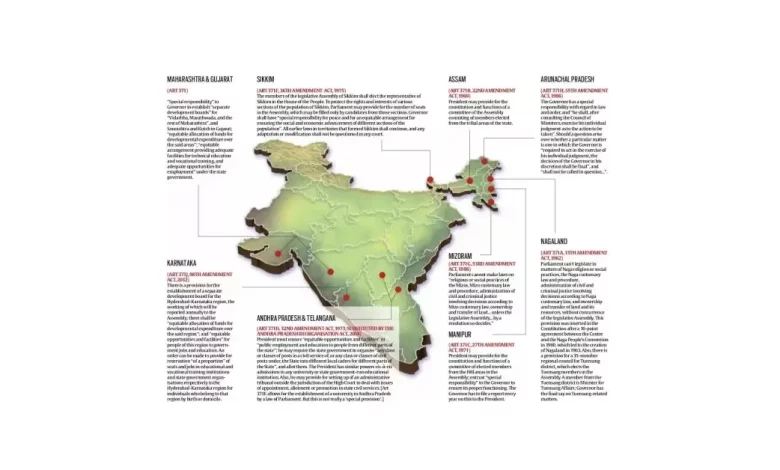
Context- The Indian Constitution creates special provisions for nine states under the Article 371A-I.
Key Highlights
- The states of Jammu and Kashmir enjoy special status under Article 370 of the Constitution, but several other states enjoy varying degrees of autonomy.
- The Constitution makes special provisions for at least nine states under Article 371A-I.
- All those exceptions are contained in the “Temporary, Transitional and Special Provisions” section of the Constitution.
- Reason: These special provisions are intended to address the unique circumstances and historical background of some states.
- States in a state of emergency often have particular rights, privileges and autonomy in certain matters.
- Reason: These special provisions are intended to address the unique circumstances and historical background of some states.
Special provisions of the constitution
- Article 371A: Special provisions for Nagaland
- A state may have its own administrative and legal mechanisms based on Naga customary laws and the right to practice religious and local social practices.
- The governor has special powers to cancel the decision of the prime minister about the public order situation.
- Article 371B: Special provisions for Assam
- The Governor of the State constituted a Legislative Assembly Committee consisting of members of the House elected by the Tribal Areas of the State.
- Article 371C: Special provisions for Manipur
- The president has the power to constitute a Tribal Mutual Legal Aid Committee through the governor.
- Article 371D: Special provisions for Andhra Pradesh
- Gives the President certain special powers over the state government, including ensuring reservation in jobs and education.
- Article 371F: Special provisions for Sikkim
- Members of the Sikkim Legislative Assembly elect the representative of Sikkim in the Lower House.
- Article 371G: Special provisions for Mizoram
- Gives people rights to their customs, religious freedom, land rights, etc.
- Article 371H: Special Provisions for Arunachal Pradesh
- Gives the governor special powers to cancel the decision of the prime minister about the public order situation.
- Article 371I: Special provisions relating to Goa
- The State Assembly of Goa has special powers to enact laws relating to the sale of land and ownership of property.
- Article 371J: Special provisions for Karnataka.
- Special powers to six backward districts under which they can form special development committees, reserve workplaces and educational institutions etc.
Difference between special category and special status:
- The Constitution grants a special status by law, which must be approved by a 2/3 majority in both chambers of the parliament, while the special category status is granted by the governing body of the government, the National Development Council.
- Special status gives legal and political rights, while special status concerns only economic, administrative and financial aspects.
Arguments In favor of the special provisions of the Constitution concerning the States
- Addressing historical injustice: Many of these provisions were included in the constitution to recognize and compensate for the historical marginalization and neglect of certain regions and communities.
- Preservation of cultural and regional identity: Special provisions are considered as a means of preserving the cultural, linguistic and regional identity of certain countries or communities.
- Promotion of Regional Development: Provisions such as reserved seats in educational institutions, labor quotas and financial incentives for economic growth and infrastructure development.
- Ensuring local autonomy: Proponents argue that special provisions provide a measure of local autonomy, allowing states to respond to their unique challenges in a more tailored way.
- Facilitation of Integration: In cases where countries have joined the Union of India through special treaties, special provisions are made to facilitate the integration process.
- Preventing disintegration: Some argue that special provisions contribute to the overall stability of the country by addressing regional grievances and preventing potential disintegration.
Arguments against special provisions of the Constitution concerning the states
- Erosion of National Unity: Uniform laws and regulations are necessary to promote a sense of national unity and integration.
- Administrative Complexity: Special provisions result in administrative complexities, as different states have different rules and regulations.
- Inequality Among States: All states should be subject to the same laws and regulations to ensure fairness and eliminate perceptions of preferential treatment.
- Potential for Regionalism: Critics express concerns that special provisions may fuel regionalism, fostering a sense of separateness and identity among certain states.
- Misuse for Political Gains: Critics argue that politicians may use these provisions to secure votes or engage in identity politics, potentially at the expense of broader national interests.
- Impediment to Economic Development: The divergence in regulations and policies may create barriers to investment and economic growth.
Way Ahead
- It is important to understand that the debate on special provisions is complex and multifaceted.
- Different stakeholders may have different views on the impact and necessity of such regulations.
- Policymakers must carefully weigh these rationales while balancing the need to address the unique circumstances of specific countries in order to promote national unity and development.
Source: Indian Express





.png)



