Context- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has assessed the diagnostic tests that will be used to screen a target group of seven crore people in order to lay out the plan to eradicate sickle cell disease in India.
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
- A debilitating systemic syndrome characterized by chronic anemia, acute pain episodes, organ infarction and chronic organ damage, and a significant reduction in life expectancy is SCD, a chronic single gene disorder.
- Because it is an inherited condition, sickle cell anemia can be passed down through families. Individuals who have the illness acquire two flawed qualities — hemoglobin S, one from each parent; One defective gene is passed down from mother to child with sickle cell disease.
- The majority of people with traits are healthy.
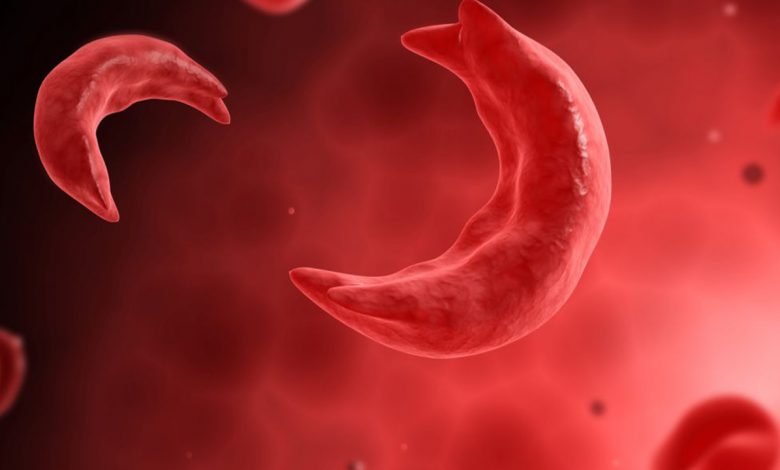
- Red blood cells that are normally flexible are transformed by haemoglobin S into rigid sickle-shaped cells, which can prevent blood flow, causing pain and damage to organs.
- According to estimates from the NHM, there are approximately 15 lakh sickle cell patients in the nation.
Symptoms:
- The signs and symptoms of sickle cell disease can vary, but some of the most common ones are:
- Anemia that persists: resulting in drowsiness, weakness, and pallor.
- Sickle cell crisis, also known as painful episodes: These can cause bone, back, arm, and leg pain that is sudden and severe.
Treatment
- Transfusions of Blood: These can assist in alleviating anemia and lowering the likelihood of pain crises.
- Hydroxyurea: This medication can help lessen the number of painful episodes and prevent some of the disease’s long-term side effects.
- Additionally, it can be treated with stem cell or bone marrow transplants.
Government Initiatives to Address SCD:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has approved the efficacy of existing Indian-made point-of-care tests through a health technology assessment.
- State governments have since been trained on these point-of-care tests, their rates, and the potential symptoms that might be common among the 7 crore people who will be screened.
- Through the National Health Mission, the Ministry of Health will provide financial support to state governments.
- The level of screening, which can be one level or two levels, is up to the state governments to decide.
- In addition, as a point of reference for technical guidance, the Health Ministry has designated the ICMR, the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), and medical colleges as nodal agencies for each State.
- The NHM has estimated that the entire screening process will cost 542.5 crore rupees.
- The management portal for sickle cell disease has already been established, and State governments have begun receiving orientation and training for the mobile application.
- The outreach component of the mission will be examined by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, which will include communication with stakeholders, the creation of training guidelines for trainers, raising awareness, non-medical patient care, and genetic counseling.
- In 2016, the government issued technical operational guidelines for the prevention and management of hemoglobinopathies, such as sickle cell anemia.
- In addition, 22 tribal districts have established integrated treatment and diagnosis centers.
- In order to address the difficulties associated with the disease’s screening and treatment, Madhya Pradesh has established the State Haemoglobinopathy Mission.
Way Ahead
- The fact that the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana provides free treatment for sickle cell disease must be widely known.
- Healthcare professional partnerships would make it easier for national assimilation and knowledge sharing.
- The significance of including pregnancy screening and making Hydroxyurea and the pneumococcal vaccine readily available.
- It is needed to raise awareness of sickle cell disease and promote “opportunity testing,” as this would speed up treatment for those already afflicted.
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs’ role in mobilizing the community and collaborating with stakeholders to determine the means of reaching affected tribal areas.





.png)



