Opportunity to Recast India’s Food System
[GS Paper 3 - Indian Economy, Agriculture and related issues]
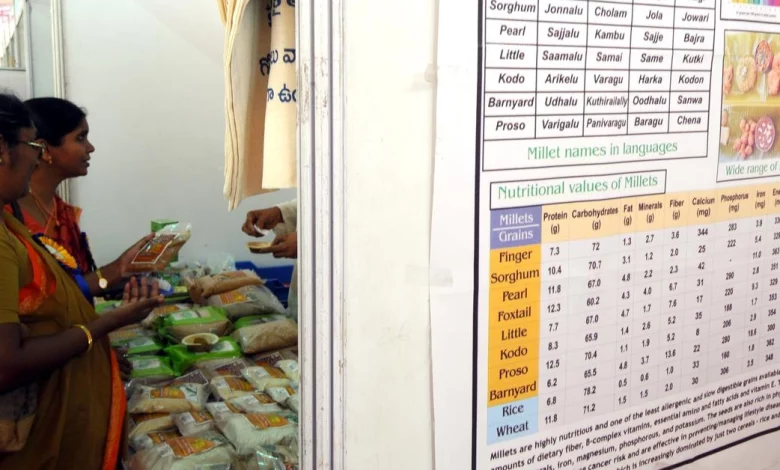
Context – World Food Day underscores the challenges of India’s food system, which caters to the world’s largest population. India, with its enormous population, faces unique challenges in ensuring a sustainable and resilient food system. This system must not only guarantee nutrition security but also provide reasonable economic returns for food producers while safeguarding the environment.
Current Scenario
India’s food system is vast, complex, and diverse, but it also grapples with significant issues. Despite being one of the world’s largest food producers, millions of Indians still suffer from hunger and malnutrition. The food supply chain is riddled with inefficiencies, leading to food wastage and loss, while the farming community often struggles with low incomes and inadequate access to resources. It is imperative that these issues are addressed to ensure food security for all.
Challenges in the Indian Food System
- Food Security and Nutrition: Food security remains a critical concern in India. Despite having sufficient food production, distribution, and storage challenges persist, leading to unequal access to nutritious food. The nation continues to face malnutrition and related health issues.
- Agricultural Sustainability: India’s agriculture sector is heavily dependent on traditional farming practices, leading to soil degradation and declining productivity. The excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides raises concerns about environmental sustainability.
- Rural Livelihoods: A significant portion of the Indian population depends on agriculture for their livelihoods. Unfortunately, many farmers face financial distress, indebtedness, and lack of access to modern agricultural practices and technologies.
- Food Wastage: A substantial portion of India’s food production is wasted due to inadequate storage, inefficient supply chains, and post-harvest losses. Addressing food wastage could go a long way in improving food security.
- Climate Change: The impact of climate change on agriculture is becoming increasingly evident. Erratic weather patterns, droughts, and floods pose a significant threat to food production and food security.
Opportunities for Transformation
- Promotion of Sustainable Agriculture: Shifting towards sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming, integrated pest management, and crop diversification, can help improve soil health, increase yields, and reduce the environmental impact of agriculture.
- Investment in Research and Technology: India can invest in research and development to create drought-resistant and high-yield crop varieties. Moreover, the promotion of precision farming techniques can optimize resource use and enhance productivity.
- Revamping Supply Chain and Logistics: A more efficient supply chain is necessary to reduce food wastage. Investment in cold storage facilities, transportation infrastructure, and improved packaging can help minimize losses and ensure food reaches consumers in a timely manner.
- Promoting Smallholder Farmer Cooperatives: Encouraging the formation of smallholder farmer cooperatives can empower farmers, improve their bargaining power, and facilitate access to credit and technology.
- Enhancing Rural Livelihoods: Supporting farmers with training, credit access, and insurance options can significantly improve their income and quality of life, reducing farmer distress.
- Diversification of Diets: Educating the public about the importance of a balanced diet and encouraging diversified food production can help reduce malnutrition and related health problems.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Implementing climate-resilient farming practices and encouraging the use of renewable energy sources in agriculture can help mitigate the impact of climate change on food production.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government has recognized the importance of revamping the food system and has launched several initiatives to address the challenges:
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN): This scheme provides direct income support to small and marginal farmers, helping to improve their financial stability.
- National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): NMSA promotes sustainable agriculture practices, emphasizing soil health, water use efficiency, and crop diversification.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): This scheme provides crop insurance to protect farmers against crop losses due to natural calamities.
- National Food Security Act (NFSA): NFSA aims to provide subsidized food grains to eligible beneficiaries, ensuring food security for the most vulnerable populations.
- Mega Food Parks and Cold Chain Infrastructure: The government has invested in building infrastructure to reduce food wastage and ensure a smooth food supply chain.
Conclusion
The challenges and opportunities in India’s food system are closely interlinked. Addressing these challenges not only enhances food security and nutrition but also promotes rural livelihoods, environmental sustainability, and economic growth. The government’s initiatives, if effectively implemented, have the potential to bring about transformative changes in the food system.
SOURCE: The Hindu





.png)



