Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Marine Heatwave (MHW) events in the Arctic Ocean
Syllabus: Geography[GS Paper-1]
Context:
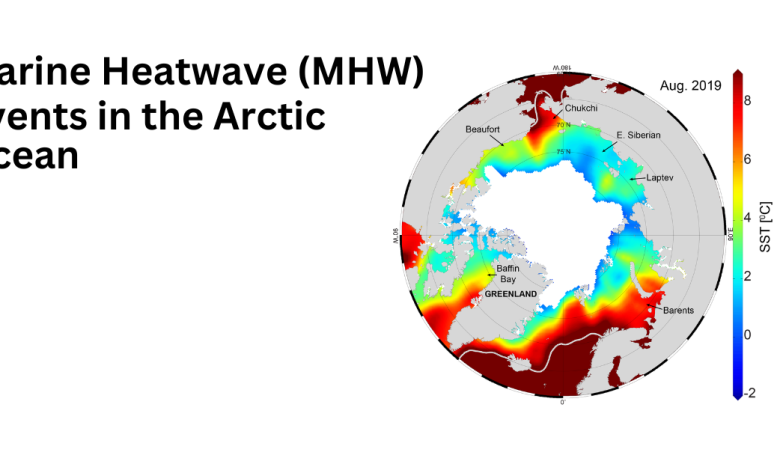
- A study in Nature Communications found that the Arctic Ocean has experienced unusual Marine Heatwave events since 2007, linked to greenhouse gases and rapid sea-ice melting.
- The research identified 11 such events between 2007 and 2021, which aligned with significant decreases in Arctic sea ice.
Key Points of the recent study:
- Marine heatwaves have been occurring in the Arctic region since 2007 and 2021, with 11 such events in 2022.
- These events, which are defined as long periods of abnormally warm sea-surface temperatures, coincide with major ice decreases in the Arctic sea.
- The Arctic Sea has seen a reduction in perennial sea ice cover since the mid-1990s, with younger, more uniformed sea ice promoting faster melting and increased solar radiation absorption.
- Marginal Seas like Kara, Laptev, East Siberian, and Chukchi are most affected by MHW events. Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a significant factor in causing moderate marine heatwaves (MHWs), with a high probability of contributing to events exceeding 1.5°C.
- Marine heatwaves can disrupt food chains, fish stocks, and biodiversity, and the use of Extreme Event Attribution (EEA) methodology can help address these consequences.
About Marine Heatwave:
- A marine heatwave is an elongated period when high temperatures above the norm occur in the ocean.
- They cause coral bleaching, damage to seagrass and reduction of kelp forests which lead to an adverse impact on the fishery industry.
- The heat waves are often from the warm surface of the ocean due to the heat from the atmosphere.
- The wind can either worsen or lessen the effects of marine heatwaves, and Pacific climate patterns such as El Nino can shift where and when these events occur.
Marine Heatwave in the Bay of Bengal:
- A marine heatwave directed the Bay of Bengal’s sea surface temperatures higher, which made more evaporation and increased the amount of moisture in the atmosphere.
- The moisture that was in excess created more heavier rainfall in the northwest India.
- In addition, the heatwave also influenced the generation and the travel of low-pressure systems known as depression formation over the Bay of Bengal.
- These depressions are very important for the monsoon pattern and rainfall distribution, and their changed behavior due to the heat-stress, shifted the rainfall more towards northwest of India.
Conclusion:
- Marine heatwaves can change the structure of ecosystems by favouring certain species and causing mass mortality events in marine invertebrates.
- Species may need to change their behaviour and habitat ranges in response to these heat waves, leading to economic losses and declines in biodiversity.
- Coral bleaching and other stressors like ocean acidification and overfishing can further harm marine ecosystems during heatwave events.
Source: DTE
UPSC Mains Practice Question:
Q.‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How will India be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India be affected by climate change? (2017)





.png)



