Context- The prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has changed significantly in India, according to a new study published in the Lancet.
Key Highlights
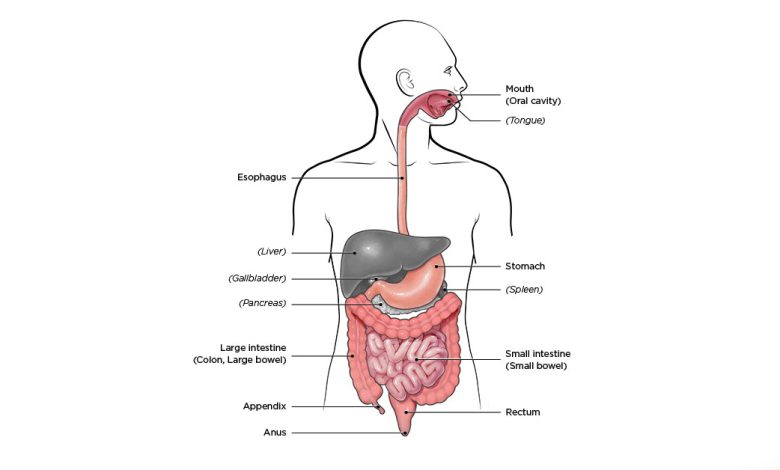
- It is a group of chronic inflammatory diseases that affect the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. These conditions cause inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive tract, leading to a variety of symptoms and complications.
- The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Crohn’s disease:
- It can affect any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus, but it most often affects the end of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon).
- Crohn’s disease inflammation can extend deep into the intestinal tissue layers and involve bypass lesions (areas separated from healthy lesions).
Ulcerative colitis:
- This type of IBD affects the large intestine (colon) and rectum. The inflammation of ulcerative colitis usually begins in the rectum and spreads continuously in the large intestine.
- The lining of the large intestine becomes inflamed, which causes ulcers to form.
Symptoms: This can vary in severity and may include:
- Abdominal pains and cramps
- Diarrhea (which may be bloody in ulcerative colitis)
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Rectal bleeding (common in ulcerative colitis)
- Joint pain and inflammation
- Skin problems
Cause:
- The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but IBD is the result of a weakened immune system. Possible reasons include:
- The immune system reacts incorrectly to environmental triggers such as viruses or bacteria that cause inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. It also seems to have a genetic component.
- A person with a family history of IBD is more likely to develop this inappropriate immune response.
Treatment:
- Although there is no cure for IBD, it is possible to reduce inflammation and treat symptoms with various treatments.
- The goal of treating IBD is to stop future flare-ups and improve inflammation in the gut, both at the mucosal and deep cellular level.
- Treatment for IBD can include medications, surgery, and various dietary and lifestyle changes to help reduce inflammation and support the immune system.





.png)



