Context- High hopes are placed on the formation of a positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and its capacity to counterbalance the El Nino effect, as the Indian monsoon is almost certain to be impacted by the El Nino phenomenon this year.
Key Highlights
- While El Nino is as of now immovably settled in the Pacific Ocean this year, the IOD is still in the impartial stage.
- As per the India Meteorological Department (IMD), the probability forecast for IOD shows around 80% probability for positive IOD conditions and 15% of a nonpartisan IOD during June-August 2023 season.
- A positive IOD event may also emerge in the upcoming months, according to all surveyed international climate models.
Indian Ocean Dipole
- The IOD is an ocean-atmosphere interaction that is very similar to the Pacific Ocean’s El Nino fluctuations and takes place in the Indian Ocean, as the name suggests.
- It is likewise a lot more vulnerable framework than El Nino, and in this manner has somewhat restricted influences.
- However, a positive IOD does have the potential to partially offset the effects of El Nino in neighboring areas, and it has done so at least once in the past (1997).
How?
- Similar to ENSO, IOD, also known as the Indian Nino, occurs in the Indian Ocean’s relatively smaller region between the Indonesian and Malaysian coasts in the east and the African coast near Somalia in the west.
- One side of the ocean, along the equator, gets hotter than the other.
Positive and Negative IOD:
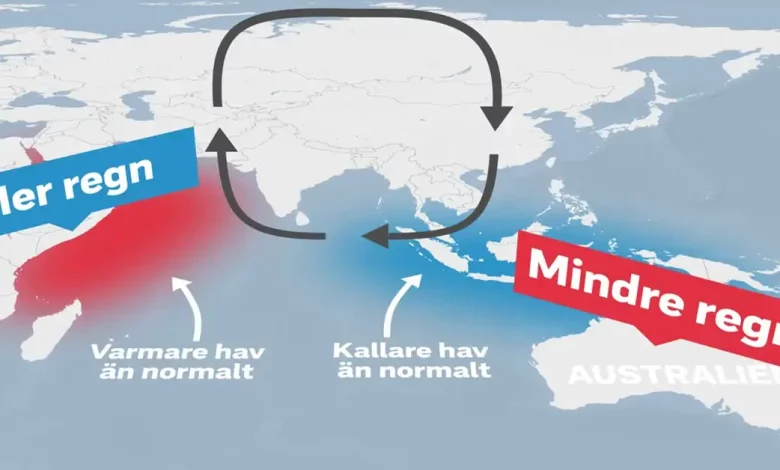
- When the western side of the Indian Ocean, near the Somalia coast, becomes warmer than the eastern side, it is said that the IOD is positive.
- When the western Indian Ocean is cooler, it is bad.
IOD and ENSO’s Relationships:
- A positive IOD event is in many cases seen creating at times of an El Nino, while a negative IOD is here and there related with La Nina.
- During El Nino, the Pacific side of Indonesia is cooler than typical due to which the Indian Sea side additionally gets cooler. That helps the improvement of a positive IOD.
- Numerous studies suggest that ENSO actually causes IOD events.
- Yet, as indicated by others, IOD occasions can have a free presence.
Effect of IOD:
- A positive IOD reduces rainfall in Indonesia, Southeast Asia, and Australia while increasing rainfall along the African coast and over the Indian subcontinent. The effects are inverse during a negative IOD occasion.
El Niño
- The term “El Nino” refers to the periodic warming of seawater in the central-east Equatorial Pacific.
- In a normal year
- The eastern side of the Pacific Sea, close to the northwestern shoreline of South America, is cooler than the western side close to the islands of Philippines and Indonesia.
- This is because the warmer surface waters are swept toward the Indonesian coast by dominant wind systems that move from east to west.
- To replace the lost water, the relatively cooler waters below rise.
- A weakening of wind systems that reduces the displacement of warmer waters is what causes an El Nino event.
Outcome
- These outcomes in the eastern side of the Pacific become hotter than expected.
- Disruptions in the food chain: Under El Nio, upwelling, in which nutrient-rich waters rise to the surface, is less common. Phytoplankton are reduced as a result.
- Accordingly, fish that eat phytoplankton are impacted, trailed by different organic entities higher up the well established pecking order.
- Disturbances in the general biological system: Tropical species are also drawn to colder regions by warm waters, disrupting numerous ecosystems.
- Adjustments in wind and atmospheric conditions: Changes in the temperature of the Pacific Ocean, which covers almost one-third of the planet, cause changes in wind patterns that disrupt global weather patterns.
- El Nio brings drought to Indonesia and Australia, dry, warm winters to the Northern United States and Canada, and an increase in the likelihood of flooding along the Gulf Coast and Southeast United States.
La Niña
- La Niña is something contrary to El Niño. La Niña is cooler than normal sea surface temperature (SST) in the tropical Pacific district.
- Exchange winds are more grounded than expected, pushing hotter water towards Asia.
- On the American west coast, upwelling increments, carrying supplement rich water to the surface.
- Jet streams, which are narrow bands of strong winds in the upper atmosphere, are being pushed northward by Pacific cold waters close to the Americas.
- This prompts drier circumstances in the Southern U.S., and heavy precipitation in Canada.
- La Niña has likewise been related with heavy floods in Australia. Australia suffered significant damage as a result of intense flooding brought on by two La Nia events that occurred in tandem over the past two years.
ENSO
- Both these circumstances, together called El Nino Southern Wavering or ENSO, influence climate occasions across the world.
Way Ahead
- IODs have much fewer effects than ENSO events, which is a long way ahead.
- However, there is still hope, as evidenced by this year’s anticipated strong El Nino in the Pacific Ocean.





.png)