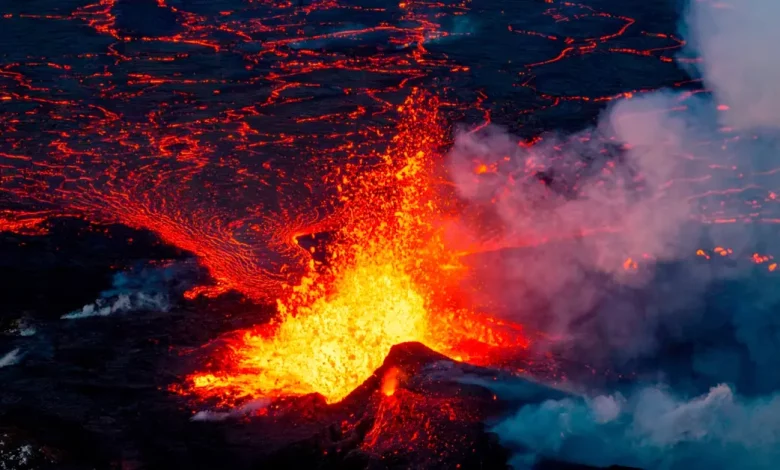
Context- Fagradalsfjall volcano located on the Reykjanes peninsula in southwest Iceland, erupted after weeks of severe earthquakes and tremors.
What are Volcanoes?
- Volcanoes are geological formations on the Earth’s crust that end result from the eruption of magma (molten rock), ash, and gases from underneath the Earth’s floor.
- Volcanoes are regularly determined close to tectonic plate limitations, where the Earth’s plates interact.
- Volcanoes may be lively, dormant, or extinct.
- Active volcanoes are volcanoes that have had current eruptions or are predicted to have eruptions inside the near future.
- Dormant volcanoes do not produce eruptions, however may again someday within the destiny.
- Extinct volcanoes will in all likelihood never erupt once more.
What are the distinct kinds of Volcanoes?
- The 3 predominant types of volcanoes are stratovolcanoes (composite volcanoes), shield volcanoes, and cinder cone volcanoes.
Stratovolcanoes (Composite Volcanoes)
- Structure: These are massive, conical mountains with steep slopes. They are characterized by means of alternating layers of solidified lava flows, volcanic ash, and other volcanic debris.
- Eruption Style: They often showcase explosive eruptions because of the excessive viscosity in their magma, which could lure gas and build up pressure.
Shield Volcanoes:
- Structure: Shield volcanoes have huge, lightly sloping profiles equivalent to a warrior’s defense. They are shaped through the buildup of low-viscosity basaltic lava flows.
- Eruption Style: Shield volcanoes commonly have non-explosive eruptions, and lava flows easily cover huge areas.
Cinder Cone Volcanoes:
- Structure: Cinder cone volcanoes are exceedingly small, steep-sided mounds built from the buildup of volcanic debris, such as volcanic ash, cinders, and volcanic rocks.
- Eruption Style: They frequently have quick-lived and comparatively explosive eruptions, generating pyroclastic cloth that falls around the vent.
Why is Iceland so volcanically energetic?
- Iceland sits on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (part of the longest mountain range within the international) inside the North Atlantic Ocean, wherein the Eurasian and North American plates are transferring aside some centimeters each yr.
- This produces volcanic rift zones, areas wherein the Earth’s crust is being pulled apart and fractured, and here molten rock, or magma, rises up, and some reaches the floor and erupts as lava and/or ash.
- The island sits over a hot sector which leads to superior volcanic activity within the vicinity.
The Pacific Ring of Fire
- The Pacific Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-formed quarter round the rims of the Pacific Ocean basin that is characterized by high seismic and volcanic interest.
- This vicinity is home to approximately 75% of the sector’s energetic and dormant volcanoes and experiences a giant number of earthquakes.
- The term “Ring of Fire ” became coined to describe this area because of the form formed by means of the several volcanoes and tectonic plate barriers.
- Countries and Regions: The Ring of Fire incorporates a large quantity of countries and areas, which include the west coasts of North and South America, components of Asia, Japan, Indonesia, the Philippines, New Zealand, and the western coasts of North America.
Source: Indian Express
Practice question:
Q. Mention the global occurrence of volcanic eruptions in 2023 and their impact on the regional environment.





.png)