Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Great Nicobar Project
Syllabus- Government Policies and Interventions [GS Paper-2]
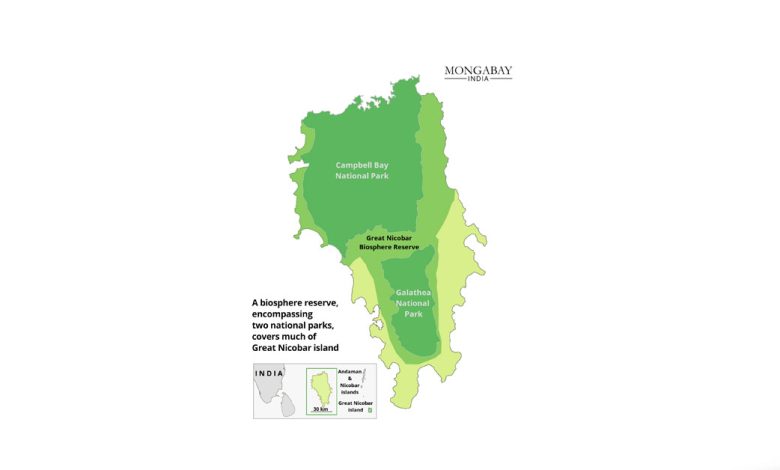
Context- The ambitious Rs 72,000 crore Great Nicobar project could cut down 9.64 lakh trees to build a transhipment port, an international airport and a 450 MVA gas and solar power plant on Great Nicobar Island.
Key Highlights
- Instead of trees being chopped, compensatory afforestation is being carried out in Haryana as “plantation area in Andaman and Nicobar is very limited”.
- 15 percent of the development area will be left green and open, which can reduce the number of trees cut down.
- Regarding the possible loss of diversity, various conservation agencies are preparing a plan for the protection or management of biological diversity.
Great Nicobar Development Plan
- Timeline: In 2022, the state granted an environmental permit to the project, which will be implemented in stages over the next 30 years.
- Organizations: The project is managed by the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO) according to the vision plan designed by NITI Aayog.
- Estimated price: 72,000 rubles.
Significance (government rationale)
- Its strategic location offers access to global trade.
- The island is located next to the Strait of Malacca, the largest choke point in the Indian Ocean.
- And its southern tip, Indira Point, is close to a major international sea route that carries about 20 to 25 percent of global maritime trade and 35 percent of the world’s oil reserves.
- A strong presence on the island is of geopolitical importance as foreigners gain a diplomatic and military foothold with neighboring countries in the important Indian Ocean region.
- This project will enhance the socio-economic growth of the local population and improve connectivity to mainland India and other global cities.
- Clean beaches, lush evergreen rainforests, picturesque hills are tourist destinations that attract sophisticated travelers.
Serious concerns raised
-
- Environment and ecology:
- The island was declared a biosphere reserve in 1989, and in 2013 it was added to the Man and Biosphere program of UNESCO.
- As a result of the project, 15 percent of the forest area will be cleared and 9.64 lakh trees will be felled in a phased manner.
- The island is home to many endemic plant and animal species that are endangered.
- According to the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) report, replacement afforestation needs to be carried out in Haryana and Madhya Pradesh due to loss of mangrove cover.
- But remote afforestation, even in areas without ecological comparison, does not make sense.
- The project will destroy huge areas of coral reefs. The EIA report recommends “transplanting” these organisms. However, transplanted corals do not have a high survival rate.
- Environment and ecology:
- Geological:
-
-
- The region is exposed to severe natural disasters.
- The island is located near the Ring of Fire and near the epicenter of the Indian Ocean earthquake in 2004, which moved the seabed vertically by 10-20 meters.
-
- About tribes:
-
- The large Nicobar Island has a population of about 8,000. Once completed, the project is expected to attract nearly 3 million people, equivalent to the current population of the entire 1,000-kilometer island chain.
- This project is against the rights of indigenous vulnerable tribal communities like Nicobarese and Shompen.
- More than three quarters of the island is designated as a tribal reserve under the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (Protection of Indigenous Tribes) Amendment Ordinance, 1956.
- This means that the land is for the exclusive use of the community and others cannot access the area. without their express permission.
Conclusions
- GDP growth should be reconsidered if it leads to an irreversible loss of natural capital.
- As the Great Nicobar Project progresses, the delicate balance between development and ecological conservation is being closely monitored.
- Government assurances on biodiversity protection and replacement afforestation are under review as stakeholders and environmentalists closely monitor the implementation of the project.





.png)



