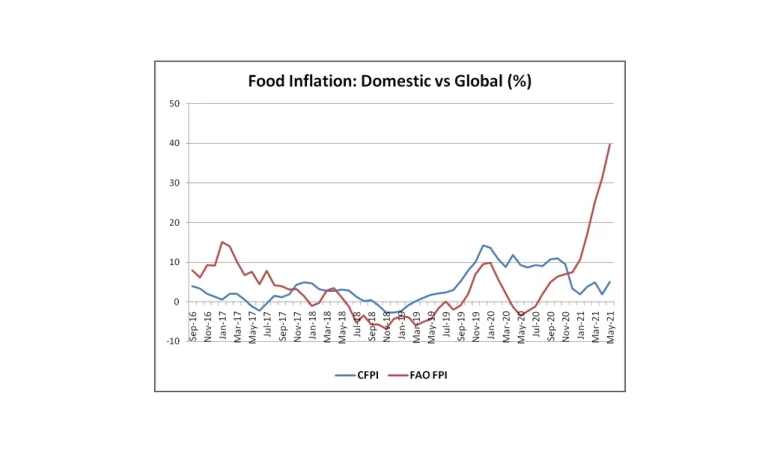
Context- In August 2023, consumer prices of food were 9.9% higher than in the same month last year. The overall retail inflation at 6.8 percent is well above the 4 percent target and the upper tolerance limit of 6 percent.
What is inflation?
- Inflation is essentially a general increase in the prices of goods and services and a decrease in people’s purchasing power.
- This means that when inflation rises (without a corresponding increase in income), you can buy fewer things than you had in the past, or you have to pay more money for the same things now.
- “Rising” inflation means that the rate (at which prices rise) is itself increasing.
- In other words, imagine a scenario where inflation was 1% in March, 2% in April, then 4% in May and 7% in June.
Measuring Food Inflation in India:
- Each price index can basically be calculated based on producer, consumer or wholesale prices, each of which has a different purpose.
- The product price index measures the average selling prices of domestic producers of goods and services.
- This differs from other measures of inflation, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures average prices from the perspective of the consumer. Seller and consumer prices may vary; for example due to taxes, subsidies and market costs.
- The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) ideally measures average wholesale market prices; i.e. where goods are sold in bulk.
- These price indexes measure the average change over time in the sales prices received by producers (product index inflation) or the prices paid by consumers (CPI inflation) or the average price change in the wholesale market (WPI inflation).
What is the Wholesale Price Index?
- The Wholesale Price Index, or WPI, measures changes in the prices of goods that wholesale companies sell and wholesale to other companies.
- The wholesale market is only for goods, services cannot be purchased at the wholesale level.
- It is used to monitor supply and demand dynamics in industry, manufacturing and construction.
- The Economic Adviser of the Ministry of Trade and Industry publishes the index every month.
- The monthly growth rate of WPI is used to measure the level of wholesale inflation in the economy.
How is WPI calculated?
- The index is based on the wholesale prices of several commodities.
- Items are selected according to their importance in the region.
- These represent different levels of the economy and are expected to provide a comprehensive WPI value.
- Number of items: 697 items
- Base year: 2011-12
Main components of WPI
- “Major Products” (22.62%) is a major part of WPI and is further divided into Food and Other Products:
- Foods: Cereals, whole wheat, vegetables, legumes, fruits, milk, eggs, meat and fish, etc.
- Non-foods: oilseeds, minerals and crude oil.
- The next major WPI basket is Fuel and Power (13.15%), which tracks price changes in petrol, diesel and LPG.
- Industrial products make up the largest shopping basket (64.23%).
- It includes several manufactured products such as textiles, clothing, papers, chemicals, plastics, cements, metals and more.
- The basket of industrial products also includes industrial foods such as sugar, tobacco products, vegetable and animal oils and fats.
What is headline and core inflation?
- Headline inflation refers to the change in value of all items in the shopping basket.
- Core inflation excludes food and fuel from headline inflation.
- Because fuel and food prices fluctuate and create “noise” in the inflation calculation, core inflation is less volatile than headline inflation.
- Headline inflation is more important in developing countries like India, where fuel and food account for 30 to 40 percent of the basket.
What is the main difference between WPI and CPI?
- The WPI tracks the wholesale price of goods, while the Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures the average price that households pay for a basket of different goods and services.
Why did the Reserve Bank of India adopt CPI and not WPI?
- As per the recommendation of the Urjit Patel Committee (2014), the RBI has chosen the CPI as the main indicator of inflation.
- In the past, RBI has given more weightage to WPI as the main measure of inflation for all policy purposes.
- CPI focuses on the change in the cost of living at the consumer level, while WPI focuses on economy-wide inflation.
- For ordinary people that is. consumers, CPI is more important than WPI.
- The CPI also covers the service sector.
- The CPI enables the RBI to increase its control over monetary policy and better monitor inflation.
- Therefore, the RBI has linked the CPI to set interest rates in India.
Role of the Monetary Policy Committee:
- Based on the recommendations of the Urjit Patel Committee, a six-member Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) was formed to fix the policy rate or repo rate.
- By an amendment to the Bank of India Act in 1934, the commission was given the status of a statutory body.
- With this, India joined the ranks of countries that have adopted inflation targeting as a monetary policy framework since New Zealand in 1990.
- On August 5, 2016, the Council of State announced in the Official Journal of the European Union that the consumer price inflation target index (KPI) for the period from August 5, 2016 to March 31, 2021 is 4% (within the tolerance of ± 2%).
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure that examines the weighted average of the prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, such as transportation, food, medical care, etc.
- Changes in the consumer price index are used to estimate price changes related to price changes.
Cost of living MPC configuration:
- The commission consists of six members (including the chairman) – three RBI officers and three foreign members appointed by the Government of India.
- The RBI Governor chairs the committee.
- The term of office of the members proposed by the government is four years from the date of appointment.
- No candidate of the Central Government shall be eligible for reappointment.
- The committee meets quarterly, i.e. every three months.
- The decisions are made by majority vote and each member has the right to vote.
- In case of a tie, the vote of the president is decisive.
Source: Indian Express
Practice question:
Q.What are the factors responsible for food inflation in India? How does food inflation impact the farmers? Examine.





.png)