Context: The World Health Organization (WHO) reaffirmed its dedication to preventing and addressing female genital mutilation (FGM) on February 6th, which is observed as the International Day of Zero Tolerance for FGM.
Key Points:
- The United Nations is reaffirming its dedication to stopping and addressing female genital mutilation.
- They are committed to the agreements set forth in various international declarations and conventions, such as the Beijing Declaration, the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women, and the Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- This commitment is also aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals, specifically target 5.3.
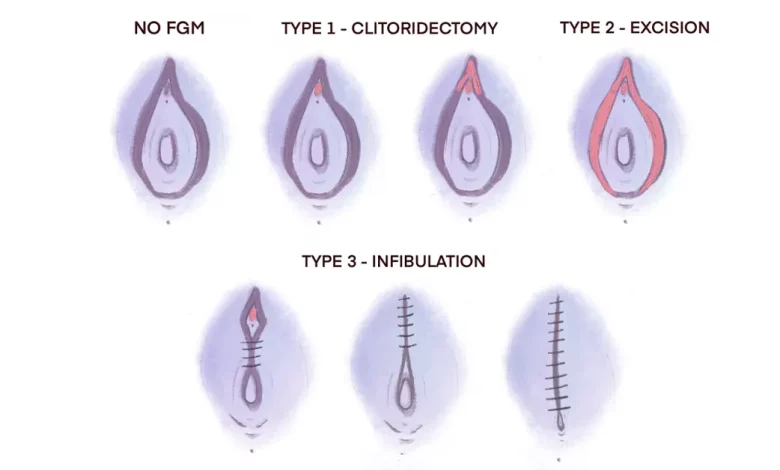
Female Genital Mutilation (FGM):
- Female genital mutilation (FGM) is a harmful practice where the external female genitalia are partially or completely removed without medical reasons.
- This practice violates human rights and can have serious physical and psychological consequences.
- FGM is commonly performed on girls between infancy and age 15 and is rooted in social and gender norms that aim to control female sexuality.
- The World Health Organization estimates that over 200 million girls and women have undergone FGM in countries primarily located in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia.
- However, FGM also occurs in some countries in Latin America, Europe, North America, Australia, and New Zealand within immigrant communities.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has increased the risk of FGM for many girls due to factors such as school closures, economic hardships, social isolation, and reduced access to health and protection services.
Global concerns of Female Genital Mutilation (FGM):
- There is no accurate figure as to the number of girls and women who have undergone female genital mutilation worldwide, but based on data from 30 countries; at least that are about two hundred million.
- This custom is predominant in areas of Africa, Middle East and Asia.
- The number of females who may undergo this procedure has also risen proportionately with an increase in travelling across Europe, Australia and North America.
- It is a global issue, as 4.3 million girls will be at risk this year alone of neglect and abuse in countries where slavery exists throughout Asia, South Korea including Mexico, Latin America and Africa etc.
- Female genital mutilation is a human right violation of women and girls whose physical and psychological health suffers as an outcome barrier to live one’s best life.
- It raises the chances of pain, haemorrhage bleeding and infections which leads to complications during delivery.
Positive aspects of the issues of FGM:
- The practice of FGM has decreased over the past three decades though one in every three young girls aged 15-20 still undergoes female genital cut for instance data from countries with information provided indicate that fgm was prevalent among a half of all women two decade ago compared to present statistics.
- The United Nations is actively involving in the fight against FGM on and off, training physicians who are supposed to perform surgical procedures for elimination of FGM; it also supports that physical operations.
- Whereas African Women’s Organization works more educative as well as preventive, raising awareness about ill consequences of practice within several African countries.
- Even though the prevalence of FGM has declined in general, there are some countries where no progress made and even if it did decline was not consistent at all.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has warned that if present state of affairs continues there will be large number increase in girls and women undergone this FGM within next 15 years.
Conclusion:
- Female Genital Mutilation is a worldwide problem that needs to be addressed with a comprehensive and culturally sensitive approach.
- It is crucial for governments, NGOs, and international organisations to continue their efforts in order to ensure the rights and welfare of women are upheld and safeguarded.
Source: DTE





.png)



