Daily Current Affairs for UPSC
Estimated Timescale for the collapse of the Gulf Stream
Syllabus- world Relations [GS Paper-2]
Context- In a recent study, scientists have estimated a timescale for the collapse of the Gulf Stream between 2025 and 2095, with a central estimate of 2050, if global carbon emissions are not regulated.
About Gulf Stream
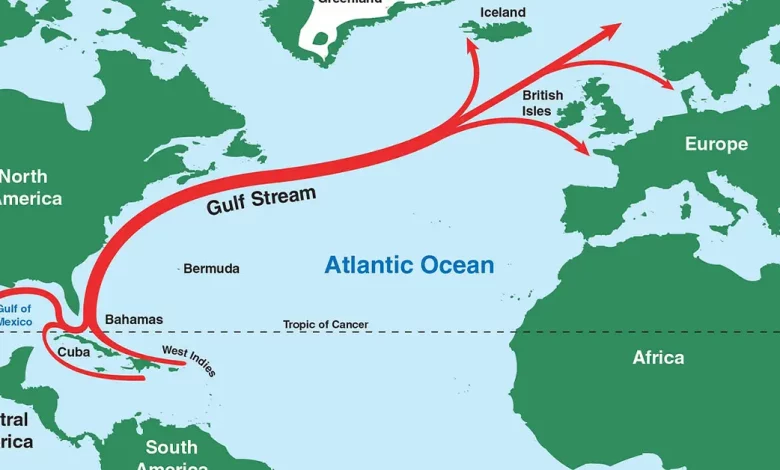
- It is a swift and warm ocean current that flows along the eastern coast of North America and crosses the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe.
- This extension toward Europe is called the North Atlantic drift.
- The Gulf Stream transports greater water than all the world’s rivers combined.
Key features
- Location: It originates in the Gulf of Mexico. It then travels northward along the eastern coast of the US. It follows a north-eastward course throughout the western North Atlantic Ocean.
- Sources: The equatorial sources of the Gulf Stream are the North Equatorial Current (NEC), which flows generally westward along the Tropic of Cancer, and the South Equatorial Current (SEC), which flows westward from southwestern Africa to South America after which northward to the Caribbean Sea. Together, those two warm currents, together with waters from the Gulf of Mexico, form the Gulf Stream.
- Warmth: The current contains warm water from the tropics (around 25 to 28°C or 77 to 82°F) to higher latitudes.
- Width and Speed: The Gulf Stream is several hundred kilometres huge and might drift at an average pace of about four miles per hour (6.4 kilometres per hour). However, its pace can vary depending on the location and other factors.
- Depth: The current is also very deep, extending to depths of up to 1,000 metres.
Importance and Impact
- Climate Regulation: It moderates the temperatures along the eastern coast of North America, retaining the coastal regions hotter in winter and cooler in summer season compared to inland areas at the equal latitudes. Since the Gulf Stream additionally extends toward Europe, it warms Western European world locations as well.
- Weather Patterns: The warm and wet air above the Gulf Stream can lead to the formation of low-pressure systems, which may grow to be storms or hurricanes. It can also contribute to the formation of fog in certain regions.
- Maritime Navigation: The Gulf Stream has been an essential element in maritime navigation for hundreds of years. It presents a quick and green route for ships traveling among North America and Europe, as it aids in quicker tour times because of its pace.
- Ocean Circulation: The Gulf Stream is an essential part of the larger oceanic circulation system known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). The AMOC performs an important function in redistributing heat across the Earth and regulating global climate patterns.
Source: The Hindu
UPSC Mains Practice Question:
Q.What is the Gulf of Mexico? How will the rising global carbon emission be responsible for its decline?





.png)



