CAPEX and the Crucial Role of States
[GS Paper 3 - Indian Economy, Government Budgeting]

Context – The budget’s clear thrust towards capital expenditure is evident in the 33% increase in its allocation. The primary goal of this allocation is to bolster aggregate demand in the short term and enhance the economy’s productive capacity in the long term.
This strategy is widely regarded as beneficial, especially considering the crucial role that infrastructure plays in the growth and development of any economy.
Capital Expenditure of the States
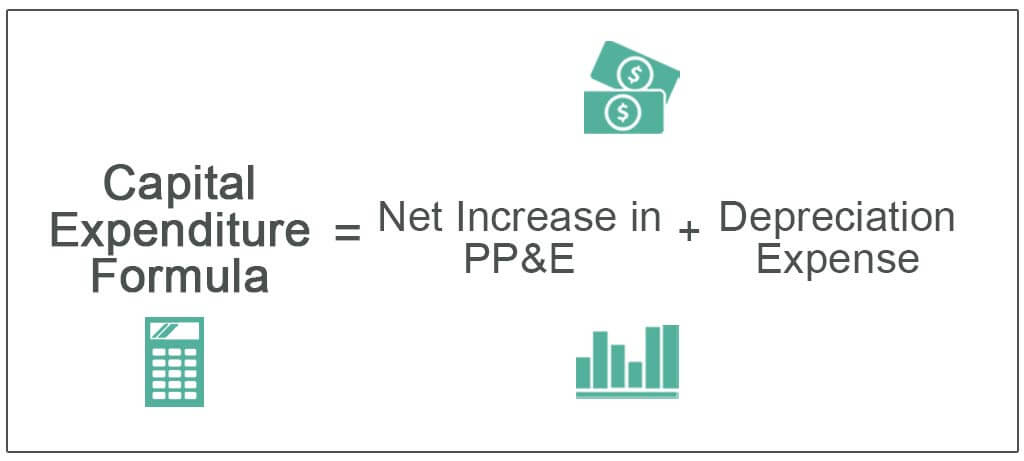
- Capital expenditure refers to investments in upgrading existing or building new physical assets by the government or private businesses. As businesses expand, capex has a multiplier effect on the economy, creating demand and unleashing animal spirits.
- Capital expenditure refers to investments in upgrading existing or building new physical assets by the government or private businesses. As businesses expand, capex has a multiplier effect on the economy, creating demand and unleashing animal spirits.
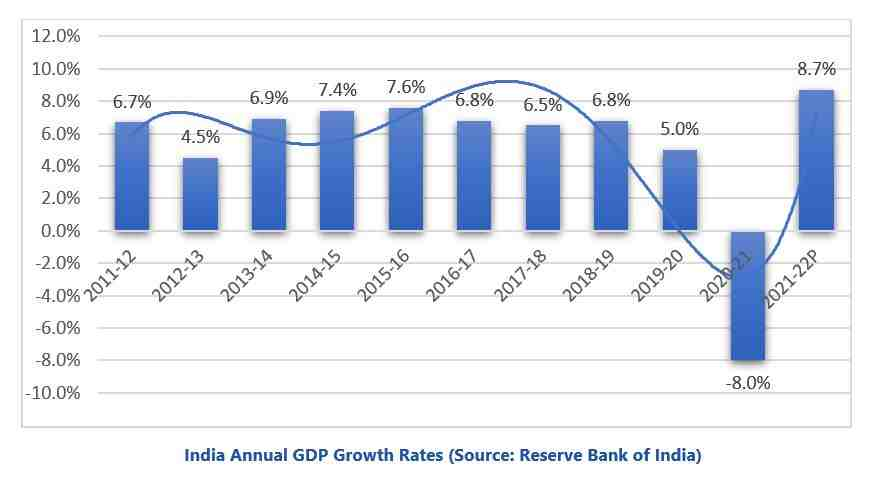
- Capex of the states exceed the central government. The combined spending of Indian states on capital expenditure now exceeds that of the central government.
- For example: In 2021-22, this figure combined for states and Union territories, according to budget estimates, was ₹10.5 trillion. The Centre’s effective capital expenditure that year was ₹8.4 trillion, including ₹2.5 trillion as grant for creation of assets.
Types of CAPEX
- Infrastructure development: This includes building and upgrading public infrastructure such as roads, highways, railways, ports, airports, power plants, and water supply systems.
- Defence and security: This involves the acquisition and maintenance of defence equipment, weapons systems, and other security-related investments.
- Social sector spending: This includes investment in areas such as education, healthcare, and social welfare programs to improve the quality of life of the citizens.
- Rural development: This includes spending on agricultural and rural infrastructure such as irrigation systems, rural electrification, and rural housing.
- Capital investments in public sector enterprises: The government may also invest capital in public sector enterprises to improve their efficiency and profitability.
Reasons behind Emphasis on CAPEX
- Promoting economic growth: Capital expenditure is critical for promoting economic growth by creating demand for goods and services, boosting private sector investment, and increasing employment opportunities. By investing in infrastructure, the government can provide the necessary framework for businesses to grow and thrive.
- Improving public services: Capital expenditure is required to build and upgrade public facilities such as hospitals, schools, and water supply systems, and provide necessary equipment and supplies. This investment in public services is crucial for improving the quality of life of citizens and promoting social and economic development.
- Infrastructure development: It is critical for promoting trade, commerce, and investment, and improving the country’s overall competitiveness. By investing in infrastructure, the government can create new economic opportunities, support the growth of existing industries, and attract foreign investment.
- Creating employment opportunities: Capital expenditure creates employment opportunities in the short term through the construction of infrastructure projects and in the long term by supporting economic growth and promoting private sector investment.
- Attracting private sector investment: The government’s emphasis on Capex can also help attract private sector investment by providing the necessary infrastructure and a favorable business environment.
Concerns over Capex
- Uneven capacity CAPEX: One general macroeconomic challenge is to address this uneven inclination of states or capacity for capital expenditure, which adds uncertainty to the impact of an expansionary fiscal policy led by capex, thus weakening its potential benefits.
- The ultimate aim of all CAPEX is to enhance the productive capacity of the economy: The nature of state capital expenditure drawn in is also vitally important. Ideally, the nature of state capital expenditure drawn in by central capital expenditure should be such that it dovetails with the latter to optimize long-term enhancements of economic capacity.
- States have tendency to postpone capex: The Union budget for 2023-24 encourages states to make reforms in urban local bodies to become creditworthy for municipal bond issuance. However, states have a tendency to postpone capital expenditure until revenue streams firm up.
Way Forward
- States need to improve their execution capacity and establish an enabling regulatory environment to ensure quality and speed of expenditure.
- The planning and budgeting cycle of states should also be aligned with fund releases to fully utilize resources within the available time.
- States play a crucial role in capital expenditure and must not only budget more but also spend fully and uniformly throughout the year.
Conclusion
States need to prioritize timely and efficient execution of capital expenditure and fully utilizing budgeted capital amounts uniformly throughout the year. The RBI report, while acknowledging that Indian states made higher capital outlays in 2022-23, notes that states would do well to mainstream capital planning rather than treating them as residuals and first stops for cutbacks in order to meet budgetary targets.





.png)



